Articles Gallery: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
[[File:Heart.glb|300px|link=Heart]] | [[File:Heart.glb|300px|link=Heart]] | ||
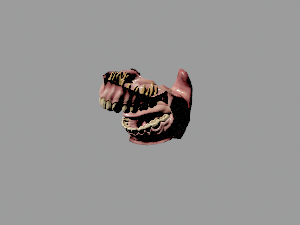
[[File:Human_mouth_detailed.glb|300px|link=Human_mouth]] | [[File:Human_mouth_detailed.glb|300px|link=Human_mouth]] | ||
[[File:Model_of_a_human_brain.glb|300px|link=Human_brain]] | |||
== Incorporating Temporal Dynamics in 3D Animation Visualization == | |||
Animated 3D models can illustrate how objects or processes change over time, making dynamic developments clearer than static 3D models. By integrating the time axis, they enrich understanding of historical evolution, scientific transformations, or mechanical functions in motion. | |||
[[File:Animated_tectonic_plates_collide_loop.glb|300px|link=Tectonics]] | |||
[[File:Tohoku_earthquake_-_2011.glb|300px|link=Earthquake]] | |||
[[File:Tesseract.glb|300px|link=Tesseract]] | |||
== Architecture and Cultural Heritage == | == Architecture and Cultural Heritage == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 20: | ||
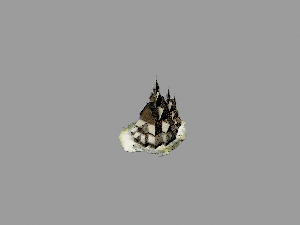
[[File:Plateau_de_gizeh.glb|300px|link=Giza_Plateau]] | [[File:Plateau_de_gizeh.glb|300px|link=Giza_Plateau]] | ||
[[File:Heddal_stavkirke.glb|300px|link=Heddal_Stave_Church]] | [[File:Heddal_stavkirke.glb|300px|link=Heddal_Stave_Church]] | ||
[[File:The_astronaut_geoglyph_in_nazca_peru.glb|300px|link=Nazca_lines]] | |||
== Astronomy and Space Science == | == Astronomy and Space Science == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 26: | ||
[[File:Solar_system.glb|300px|link=Solar_System]] | [[File:Solar_system.glb|300px|link=Solar_System]] | ||
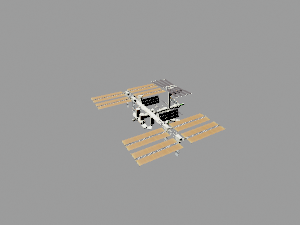
[[File:International_Space_Station.glb|300px|link=International_Space_Station]] | |||
[[File:Blackhole.glb|300px|link=Black_hole]] | |||
== Engineering and Transportation == | == Engineering and Transportation == | ||
| Line 22: | Line 33: | ||
[[File:Boeing_747.glb|300px|link=Boeing_747]] | [[File:Boeing_747.glb|300px|link=Boeing_747]] | ||
[[File:N700-3000_series_shinkansen.glb|300px|Shinkansen]] | |||
[[File:Ford_t.glb|300px|Ford_Model_T]] | |||
== Natural Landscapes and Geography == | == Natural Landscapes and Geography == | ||
| Line 27: | Line 40: | ||
[[File:Lees_ferry_grand_canyon_arizona.glb|300px|link=Grand_Canyon]] | [[File:Lees_ferry_grand_canyon_arizona.glb|300px|link=Grand_Canyon]] | ||
[[File:Mount_everest_and_mountains_tibet_nepal.glb|300px|link=Mount_Everest]] | |||
[[File:Monument_valley_-_merrick_butte.glb|300px|link=Merrick_Butte]] | |||
== Biology == | |||
3D models provide a realistic representation of objects, which helps improve understanding of their shape, function, and spatial relationships. This is especially useful for studying organisms, fossils, and anatomical features, where a detailed and accurate visualization can bring insights into its biology and evolution. | |||
[[File:Triceratops.glb|300px|link=Triceratops]] | |||
[[File:Red_Fox_Cranium.glb|300px|link=Red_fox]] | |||
[[File:Bacteriophage.glb|300px|link=Bacteriophage]] | |||
== Mathematics == | |||
3D models enable precise visualization and analysis of surface geometry, capturing curvature, texture, and topology beyond the limits of 2D representation. Some surfaces, such as the Steiner surface, are hard to visualise without a 3D model. | |||
[[File:Klein_bottle.glb|300px|link=Klein_bottle]] | |||
[[File:Mobius_strips.glb|300px|link=Möbius_strip]] | |||
[[File:Roman.glb|300px|link=Roman_surface]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:31, 25 August 2025
Explore Wikipedia articles with interactive 3D models for an immersive learning experience.
Medicine and Anatomy
Interactive 3D models in medical articles allow students, educators, and professionals to explore complex anatomical structures dynamically. This enhances spatial understanding and improves both teaching and self-directed learning in health sciences.
Incorporating Temporal Dynamics in 3D Animation Visualization
Animated 3D models can illustrate how objects or processes change over time, making dynamic developments clearer than static 3D models. By integrating the time axis, they enrich understanding of historical evolution, scientific transformations, or mechanical functions in motion.
Architecture and Cultural Heritage
For historical sites and architectural wonders, 3D models bring cultural heritage to life. They allow users to experience the design, construction, and spatial relationships of ancient and iconic structures, supporting preservation and public education.
Astronomy and Space Science
3D visualization in astronomical subjects makes vast scales and complex structures accessible. These models can illustrate orbital dynamics, spatial relationships, and the design of space missions to engage both the public and researchers.
Engineering and Transportation
Interactive 3D models allow enthusiasts, students, and professionals to explore the design and functionality of complex machines. These models illustrate key engineering principles and innovations in transportation.
Natural Landscapes and Geography
3D models of natural landscapes and geological formations provide an immersive way to appreciate the scale and intricate details of Earth’s features. They support educational initiatives in earth sciences and environmental studies by offering intuitive, visual representations.
Biology
3D models provide a realistic representation of objects, which helps improve understanding of their shape, function, and spatial relationships. This is especially useful for studying organisms, fossils, and anatomical features, where a detailed and accurate visualization can bring insights into its biology and evolution.
Mathematics
3D models enable precise visualization and analysis of surface geometry, capturing curvature, texture, and topology beyond the limits of 2D representation. Some surfaces, such as the Steiner surface, are hard to visualise without a 3D model.